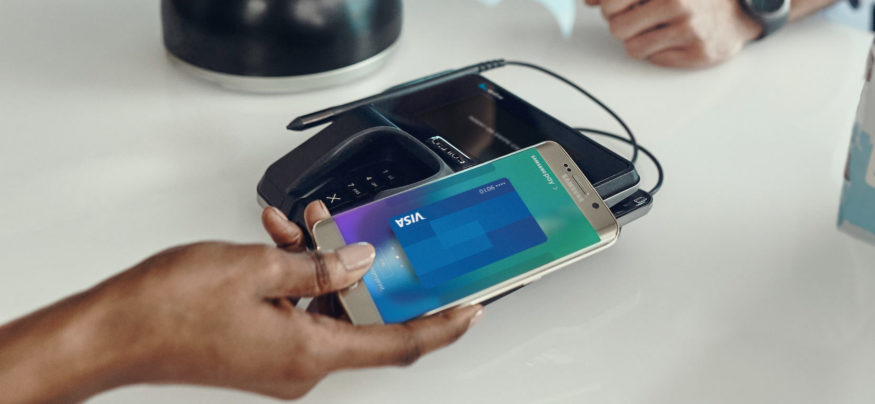
Magnetic secure transmission uses electromagnetic technology to transmit payment card data to payment terminals equipped with traditional magnetic stripe readers. In this way, it can turn traditional point-of-sale terminals into contactless payment terminals without the need to modify or upgrade them.
How It Works
The technology was developed by LoopPay, which was acquired by Samsung in February 2015 and is now the technology behind Samsung Pay. The technology incorporates a small metal coil through which electricity passes to create a magnetic field that can communicate with standard magnetic payment card readers. This allows it to emulate the process of swiping a card at a POS terminal with which many users are familiar. The Samsung Pay service also supports the use of near-field communication (NFC) technology, although this isn’t yet as widely accepted as magnetic secure transmission technology, as only a small fraction of payment terminals accept NFC payments to date. For many retailers, especially those with multiple locations, the cost of upgrading terminals to support NFC payments is prohibitive.
Magnetic Secure Transmission Boosts Mobile Payments
Up to 90 percent of retailers are able to accept Samsung Pay through existing terminals. This easy transition will do much to boost the popularity of mobile payments. When launched in South Korea in August 2015, more than 1.5 million transactions were conducted and more than $30 million was spent by consumers using the service in the first month alone. Samsung Pay is now also available in the U.S.
Ease of Use
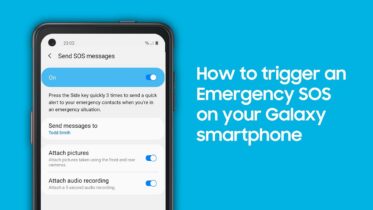
Magnetic secure transmission technology provides ease of use for consumers, who must simply hold their Samsung Pay-enabled mobile devices over the payment terminal to initiate payment. The consumer is then asked to scan their fingerprint using the built-in reader on their device, or to enter a PIN. Samsung Pay also means that consumers don’t have to carry a wallet full of credit and debit cards, since multiple cards can be registered for the service.
Built-In Security
The use of magnetic secure transmission technology is not only as secure as NFC payments; it’s more secure than traditional payment cards that just have a magnetic stripe. The technology uses tokenization, which transforms payment card information into a randomly generated set of symbols, known as tokens, that are associated with a particular transaction and that are almost impossible to reverse engineer. The actual card number is stored in a secure vault at the associated bank or payment card issuer, never on the merchant’s systems or Samsung’s.
Because security is built into the Samsung Pay system, along with the security of the magnetic secure transmission technology, the risk of identity theft and card fraud can be reduced considerably. Along with its ease of use and the fact that it provides digitization for traditional magnetic stripe payment terminals, the use of mobile devices to make payments in a wide range of retail and hospitality environments looks set to take off dramatically. Since traditional payment terminals can be used, retailers can make investments in upgrades at a time that suits them, rather than being forced to do so in order to accept mobile payments.
Learn more about innovations in point-of-sale terminals and payment technology.