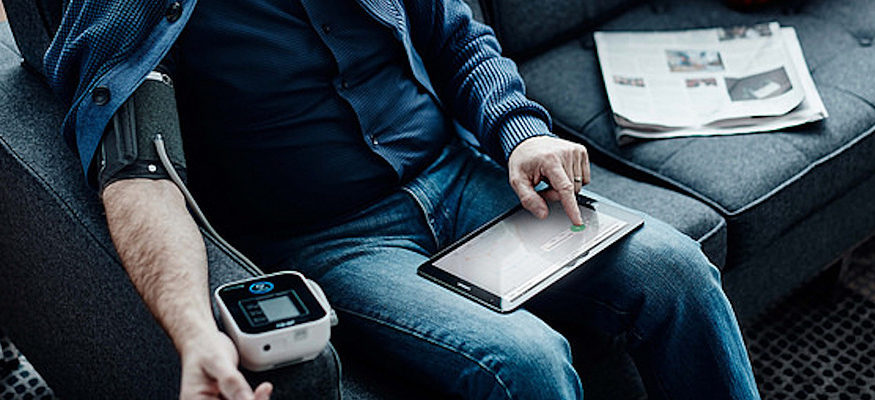
Much of the recent healthcare innovation has occured in clinical environments such as hospitals and doctors’ offices. However, the biggest potential benefits of telemedicine, and the real-time data it provides, are to patient-centric healthcare. Telemedicine has leapt out of the clinical world and is pushing into other areas including research, the home and other consumer-centric spaces, streamlining care processes and offering benefits for patients, researchers and doctors.
Telemedicine Is Changing Pharmaceutical Research
Most healthcare pharmaceutical researchers are familiar with the time- and resource-consuming challenges that come along with clinical trials — frequent office visits to gather information from subjects, constant manual tracking performed by the participants and generally unreliable data. However, thanks to an increase in the popularity of telemedicine, much of this could be changing.
With the introduction of telemedicine, participants can now be given wearable and FDA Class II medical devices, along with mobile applications and sensors — a definitively more patient-centric approach to data collection that could allow researchers to see the following benefits:
-
A streamlined decision-making process: If researchers have access to real-time data, they can make changes and amendments to protocols, as well as decisions based on drug reactions early on in the study. They can also observe early signals around a drug’s effectiveness, granting them insight into differences around specific subsets of the population, as well as a better understanding of how participant behavior impacted their results.
-
A better and more objective view of participant drug responses: If data is collected in real time, researchers have a more holistic view of each participant’s response to a drug over time and between office visits. The data collected this way is more objective and less reliant on the subjectivity of human interpretation, memory and mood.
-
Improved and more accurate intervention triggers: Adverse reactions are a dangerous reality during drug trials. Data collected in real time can alert researchers to problems much sooner. Additionally, if participants have issues around nonadherence, researchers are more likely to be alerted and can adjust as needed.
Another benefit of providing researchers with real-time access to data is increased patient enrollment. The burden of frequent office visits, having to recall information, and the annoyance of constant manual entry are a deterrent for many potential participants who might be well-suited to a study. Telemedicine solutions can change both the reality and perception of clinical studies and get more, and better-suited, participants involved.
Telemedicine Offers a Patient-Centered Future
The greatest potential of telemedicine, though, goes beyond research.
As the U.S. sees 78 million baby boomers becoming senior citizens, the country’s elderly population is expected to balloon over the next 15 years — according to The Hill, by 2030, people over age 65 will make up over a fifth of the population. Those same people have already begun to express an overwhelming desire to age in place.
While many challenges exist around meeting these desires, a patient-centric telemedicine approach is a powerful step in at least addressing the healthcare piece of the puzzle. Remote monitoring solutions that incorporate tablets, wearables and other mHealth solutions can be used to address steadily increasing chronic diseases and, when partnered with sensors and elderly-specific home design, can even create environments that constantly “read” patient health and can quickly contact care providers and emergency personnel in the case of an emergency such as a fall.
The steadily developing telemedicine environment doesn’t stop at the elderly. Healthcare leaders are beginning to understand the potential that mHealth and telemedicine have in extending healthcare beyond the clinical environment. According to mHealth Intelligence, a recent survey of healthcare executives revealed that the most popular topics around the future of telehealth are patient education/training and remote patient monitoring, indicating that the move away from clinic-centered telehealth might be ushered in by clinical entities themselves. As stated by Mike Baird, co-founder and CEO of telemedicine leader Avizia, “It’s the patient who’s taking control of telehealth, and it’s up to the IT departments and clinical departments to figure out how to catch up.”
Learn more about some innovative uses of telemedicine, such as how Children’s Health in Dallas is using it to bring remote monitoring benefits to pediatric patients, here.