Despite what you may think, one size does not fit all when it comes to solid state drives (SSDs). To understand why, it’s worth brushing up on what SSDs are and how they are used.
SSDs employ non-volatile solid state chips that feature flash memory cells designed to store data on a long-term basis. Unlike traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), which use magnetic platters spinning at high speeds and a read/write actuator arm that moves across the platter accessing and writing data, SSDs have no moving parts. Instead, they use flash memory to store files, making them much faster at reading and writing data, both ad hoc and in sustained operations.
The more flash memory cells an SSD has, the higher the capacity. Years ago, there wasn’t much choice when it came to SSD size, but advancements in SSD technology mean capacity differences now range widely. Capacity isn’t just about how much you can store. The size of your SSD — having more capacity — also changes an SSD’s speed, performance and power efficiency. Read on to learn how capacity affects what you can use an SSD for and how you can choose the best SSD option for what you need to do.
Is bigger better?
Capacity is one of the key considerations when deciding what SSD to get.
An SSD’s capacity is based on the number of NAND chips on the drive. (You may have also read about Samsung-developed V-NAND, which is a way of adding capacity to an SSD drive by stacking cells on top of each other.) Capacities range from 120GB on the low end to over 30TB on the high end, and everything in between. Most businesses won’t need any drives over 8TB, though.
Before you choose a capacity, it’s worth noting that SSDs also come in a wide variety of connection protocols and form factors. There are three main connection protocols: serial advanced technology attachment (SATA), peripheral component interconnect express (PCIe®) and non-volatile memory express (NVMe®). The difference between each of these is connection speed and the form factor of the connection end.
There are four SSD form factors: 2.5-inch, M.2, mSATA and U.2. A 2.5-inch SSD drive looks a lot like a traditional HDD and fits inside most desktops, laptops and servers, while an M.2 is much smaller but also installs inside of a system. For an ultra-slim computing device, the mSATA is ideal, while a U.2 form factor is on the larger side with higher storage.
Before you choose your capacity and device, make sure you know what kind of slots you have (and if you have any available) on your motherboard. If you prefer external SSD drives, you’ll still need to know what connection options your device uses.
Get your complete guide to SSD management
Discover how to effectively adopt and manage SSDs in your organization with this ultimate guide. Download Now
Making the right choices
What SSD size you should get really depends on what you’re looking to do with your device.
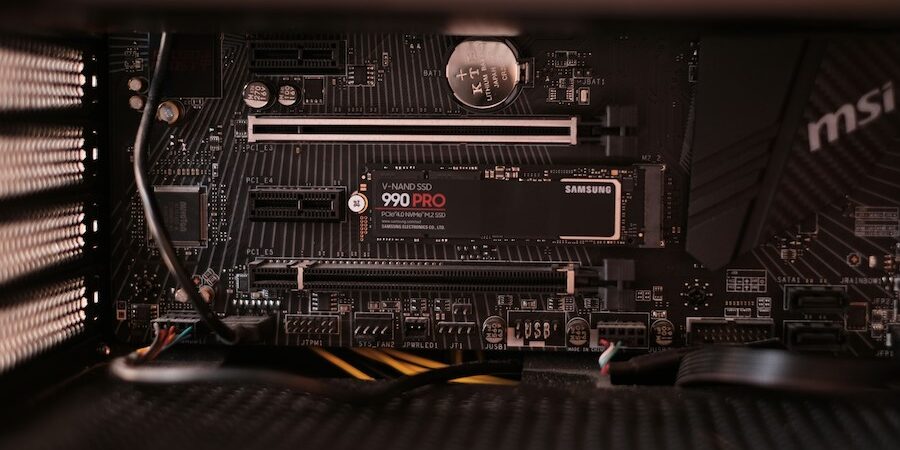
If you’re looking for an SSD to improve your gaming experience, you’ll need something with low latency to reduce lag. One option, Samsung 990 PRO4TB, is a single-sided 4TB SSD. It uses Samsung V8 1TB high-density NAND and its memory stacking technology. And since Samsung’s 4TB 990 PRO series is designed with a single-sided M.2 form factor, it’s slimmer than other double-sided M.2 SSDs, so you can use it in an ultra-slim laptop as well as a desktop.
SSDs are also great for running large applications or working with large files. For instance, if you’re looking to work with analytics or another program that requires a lot of data, such as video editing, the 4TB offering in Samsung’s SSD 990 PRO Series is a solid choice. The 990 PRO Series is optimized for massive data volumes, such as 3D/4K graphics work, data analytics and high-quality games, since it has sequential read speeds of up to 7,450 megabytes-per-second (MB/s) and write speeds of up to 6,900 MB/s.
Finally, if you’re running your own business or have your own data center, you can tap a larger SSD drive that has the added reliability for critical data thanks to end-to-end data protection. Samsung PM893 features sequential read/write speeds of up to 550/520 MB/s and random read/write speeds of up to 98,000/30,000 IOPS, which is ideal for handling massive amounts of data.
The bottom line
Figuring out what you need is not as difficult as it sounds. As a rule of thumb, consider your use case. If you’re looking for a portable SSD to store data you can work on remotely, grab a smaller 128GB drive, while anything 250GB or less will run your operating system or let you do frequent backups of your device. SSDs that have capacities between 500GB and 1TB are perfect for frequently used business applications, regular gaming and straight storage. When it comes to AI, machine learning, high-definition gaming and video editing, you’ll need more capacity — an SSD that’s 2TB or more. The type of SSD to buy will also depend on the type of device it will go into.
Browse Samsung’s acclaimed SSD offerings for the right size and form factor for your organization. To learn more about the use of SSDs in the gaming world, check out how Samsung’s SSDs support a better gaming experience.